Auditing is an important part of detecting system intrusions or malicious activity on your systems and network. The Windows Event Viewer does not log event entries in the security log unless you enable auditing on the system. This can be done easily through group policy or in the local security policy.
Solution
You can enable auditing on each Windows operating system on your network easily through Group Policy or locally. After you enable auditing, you can choose which events to monitor. Monitoring events such as successful or failed logon attempts. In addition, certain files and directories can be audited on NTFS file systems for changes.
We can achieve this locally by:
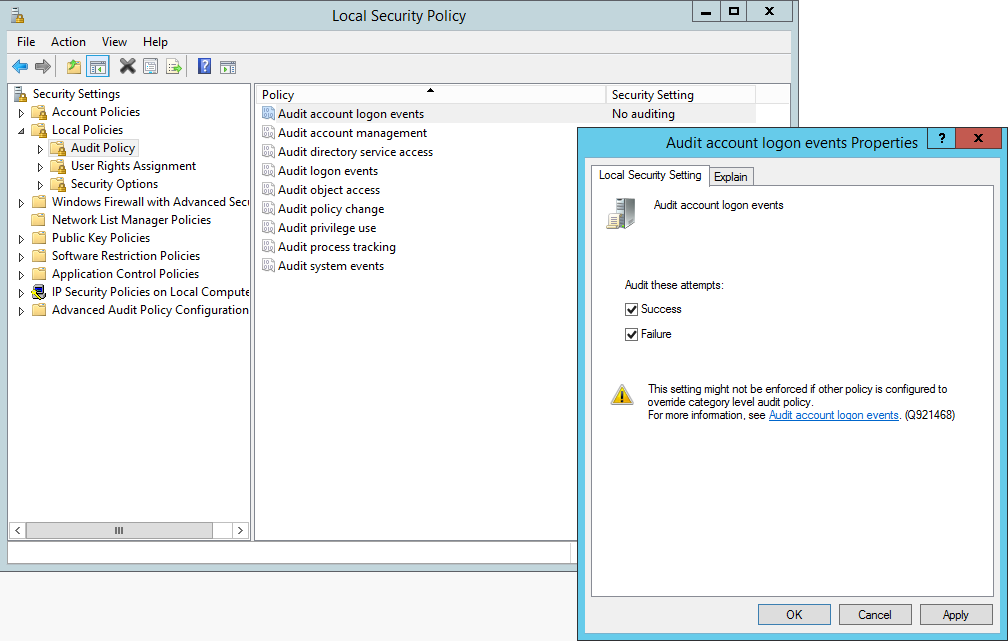
Navigate to the Local Security Policy editor. You can find this through either control panel or through: Start, run, type secpol.msc.
In Local Security Settings, double-click Local Policies, double-click Audit Policy, and then click the events that you want to audit.
A better way to manage this is through Group Policy:
Computer Configuration/Policies/Windows Settings/Security Settings/Local Policies/AuditPolicy:
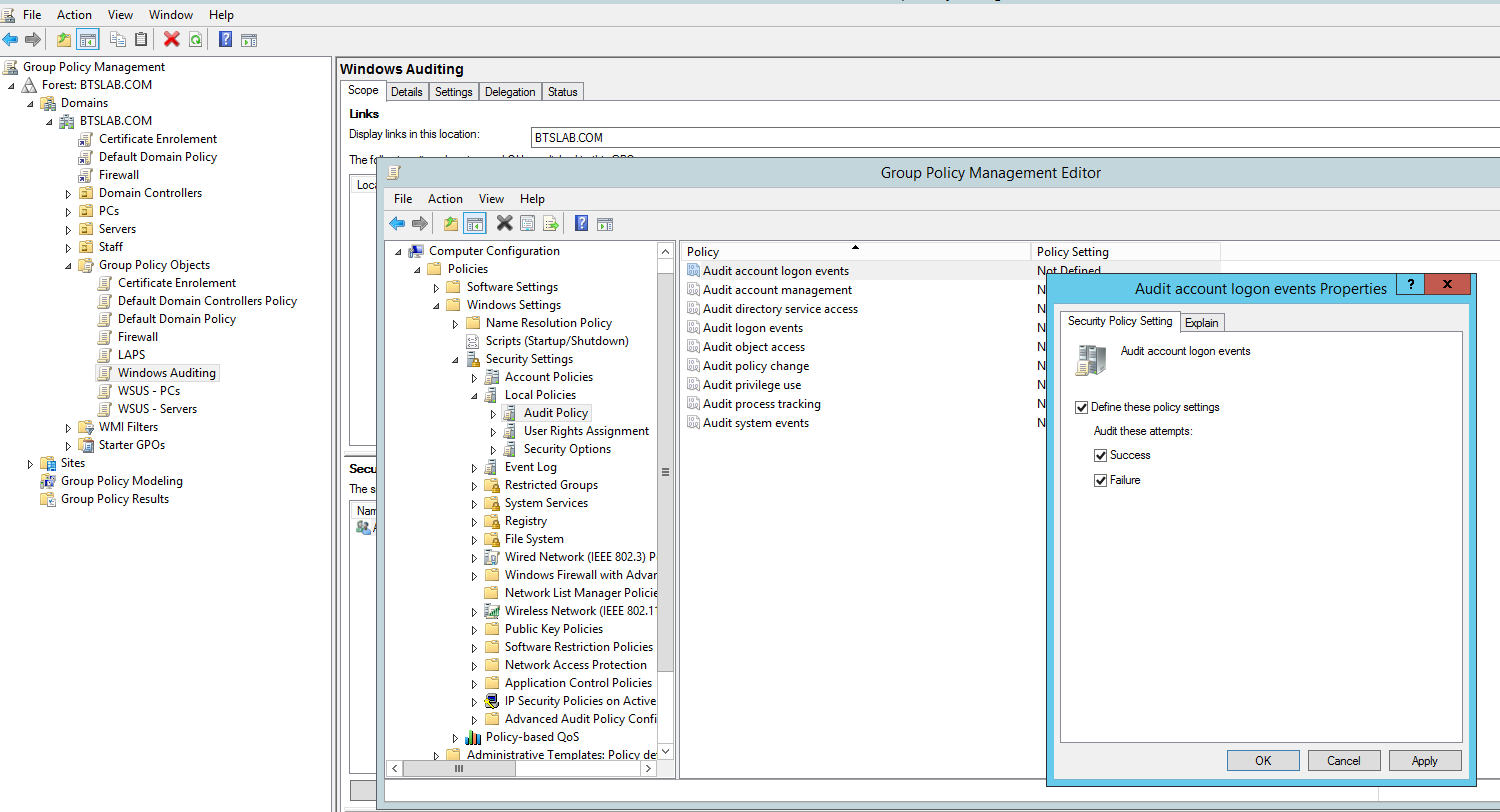
Then apply it to your computers and servers.
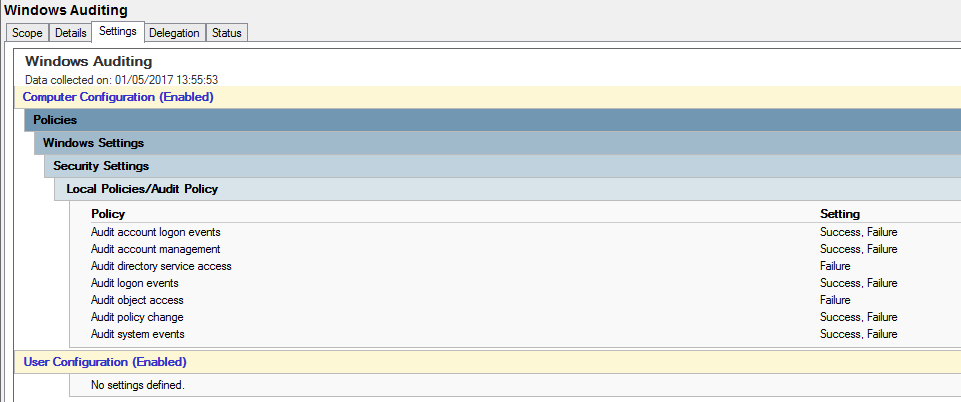
Microsoft recommends the following:
Audit account logon events (Success, Failure)
Audit account management (Success, Failure)
Audit directory service access (Failure)
Audit logon events (Success, Failure)
Audit object access (Failure)
Audit policy change (Success, Failure)
Audit system events (Success, Failure)
The Center for Internet Security CIS benchmarks have recommendations per operating system. For example the CIS benchmarks for Windows Server 2012 R2 located here recommends the following.
