Server Message Block SMB Signing is a security mechanism used in windows for digitally signing data at the packet level. Digitally signing the traffic enables the client and server to verify the origination and authenticity of the data received.
SMB signing can either be set through Group Policy Objects (GPO) or in the registry. Whilst this does increase security for clients and servers it does have a performance hit requiring extra computational power to deal with the hashing involved. This should be taken into consideration when looking into enabling this option, further more this should be tested out thoroughly before changing in a production environment. Domain Controllers (DC) digital sign there communications by default, this is set in the ‘Domain Controllers’ GPO however member servers and clients do not have this set (other than communication to the DC).
This Post will go through the different options to enable SMB signing for both Windows server and workstation.
SMB Signing through the Registry
To enable this in the registry we need to create the following client registry key and amend the value data to 1 (ie to switch on):
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanWorkStation\Parameters\RequireSecuritySignature
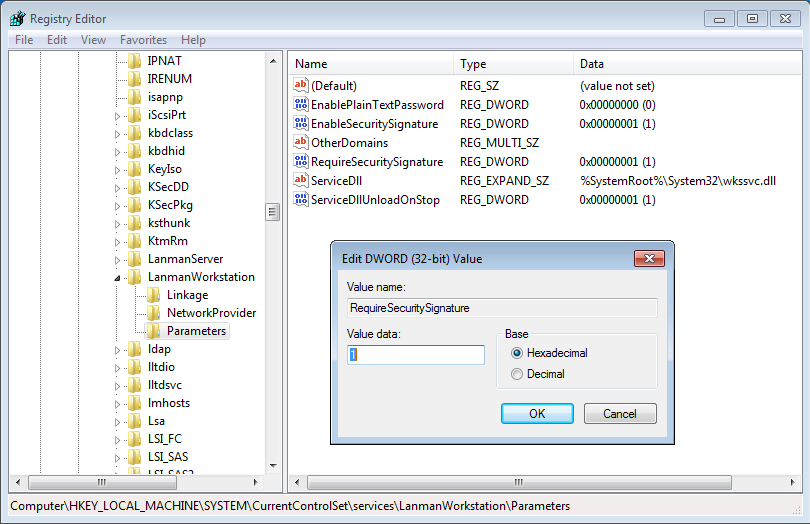
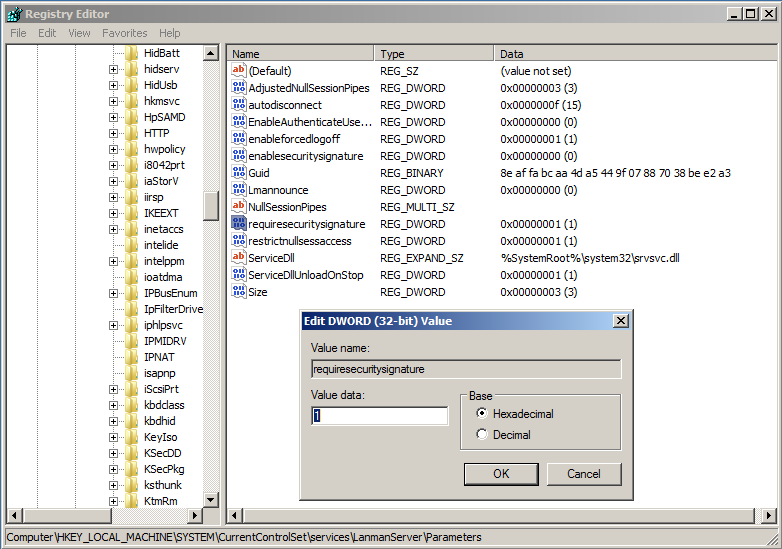
Server registry key is:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters\RequireSecuritySignature
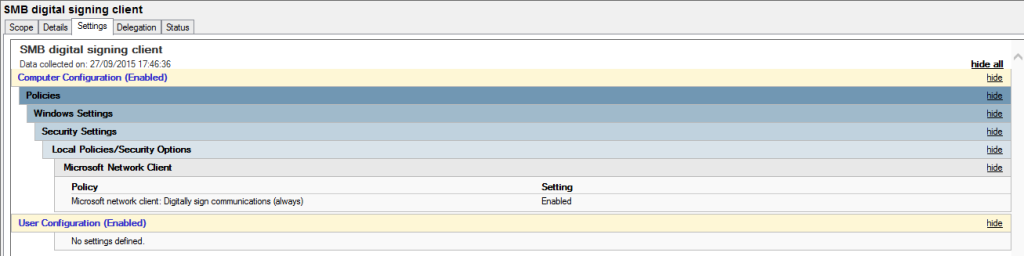
SMB Signing through Group Policy
In order to set via a group policy object you will need to create a new policy and change the below settings for the client:
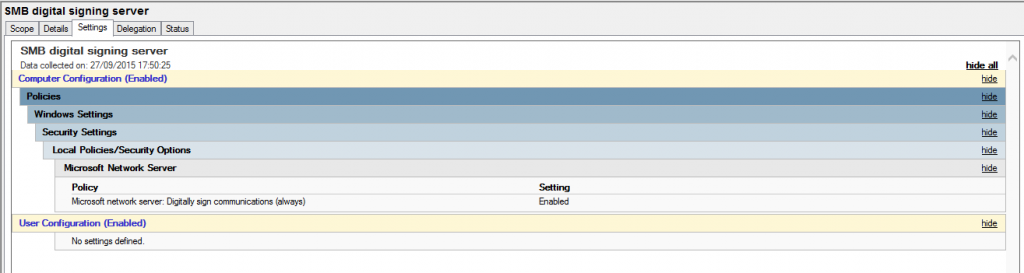
And for the server:
It clearly goes without saying you should first test these methods for yourself in a safe test environment first before diving into your main production domain environment.
